Hard core vitenskap popularisering
ISP (image signal processor)
DSP (Digital Signal Processor)
ISP is generally used to process the output data of the Image Sensor, such as AEC (Automatic Exposure Control), AGC (Automatic Gain Control), AWB (Automatic White Balance), color correction, Lens Shading, Gamma correction, bad spot removal, Auto Black Level, Auto White Level, etc.
DSP has more functions than ISP. It can take photos and echo (JPEG encoding and decoding), video recording and playback (Video encoding and decoding), H 264 encoding and decoding, and many other aspects of processing, in short, processing digital signals. ISP is a special kind of DSP that processes image signals.
01.ISP Image Signal Processor
The main function of ISP (Bildesignalprosessor) image signal processor is to process the signal output by the front-end image sensor in the later stage. Different ISPs are used to match image sensors from different manufacturers.
The excellence of ISP is very important in the whole camera product. It should be said that it directly affects the image quality presented to users. After the image is collected by CCD or CMOS, it needs post-processing to better adapt to different environments, and can better restore the field details under different optical conditions.
In ISP, it will complete the 2A (AWB/AE, auto white balance/auto exposure) or 3A (AWB/AE/AF, auto white balance/auto exposure/auto focus) that we often mention. In traditional mode, a DSP or an FPGA is usually used to complete the post-processing of images. Some camera products support 3D noise reduction, wide dynamic, slow shutter, frame accumulation, strong light suppression and other functions that are also completed by ISPs.
ISP architecture scheme: it can be divided into two forms: independent (external) and integrated (internal).
CPU processors include AP, BP and CP. BP: baseband processor, AP: application processor, CP: multimedia accelerator.
02.ISP’s main internal composition
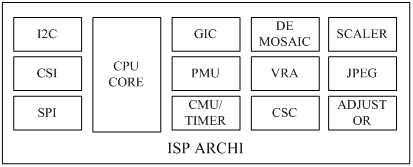
As shown in the figure below, ISP includes CPU, SUP IP, IF and other devices. In fact, ISP can be considered as a SOC (system of chip) that can run various algorithm programs to process image signals in real time.
CPU
The CPU is the central processing unit, which can run various image processing algorithms such as AF, LSC, and control peripheral devices. The internal CPU of modern ISP is generally ARM Cortex-A series, such as Cortex-A5 and Cortex-A7.
SUB IP
SUB IP is a generic term for various functional modules, which process images professionally. Common SUB IP, such as DIS, CSC, VRA, etc.
Image transmission interface
There are two kinds of image transmission interfaces, parallel ITU and serial CSI. CSI is the abbreviation of MIPI CSI. In view of many advantages of MIPI CSI, MIPI-CSI interface has been widely used to transmit image data and various user-defined data in the field of mobile camera. External ISP generally includes MIPI-CSIS and MIPI-CSIM interfaces. Built in ISP generally only requires MIPI-CSIS interface.
General peripherals
General peripherals refer to I2C, SPI, PWM, UART, WATCHDOG, etc. ISP includes I2C controller, which is used to read OTP information, control VCM, etc. For an external ISP, the ISP itself is an I2C slave device. The AP can control the ISP’s working mode and obtain its working status through I2C.
03.ISP Processing Flow
Image generation process: the scene is projected onto the sensor surface through the optical image generated by Lens, converted into analog electrical signals through photoelectric conversion, converted into digital image signals through A/D conversion after noise elimination, and then sent to the digital signal processing chip (DSP) for processing.
Therefore, the image from the sensor is a Bayer image, which has undergone black level compensation, lens shading correction, bad pixel correction, color interpolation, Bayer noise removal, white balance correction, color correction, gamma correction, color space conversion (RGB to YUV) In the YUV color space, color noise removal and edge enhancement, color and contrast enhancement, and automatic exposure control are required. Then, YUV (or RGB) format data is output and transmitted to the CPU through the I/O interface for processing.
Currently, ISPs used in high-definition camera products generally come from the following sources:
Self research and development by manufacturers: In order to better cooperate with back-end compression and function development, high-definition camera equipment manufacturers independently develop ISP processing algorithms, integrate the algorithms into FPGA or DSP chips, and connect the front-end image sensors.
Third party R&D: I 2010, a number of ISP solutions launched by non HD camera manufacturers have gradually emerged. They directly sell different ISP chips to camera manufacturers to cooperate with sensors from different manufacturers.
Overlay mode: The sensor manufacturer will combine the self-developed ISP with its own sensor to form an image acquisition and processing solution to the customer. The image processing algorithm and various debugging work have been completed. The camera manufacturer only needs to do interface docking and back-end compression or conversion to digital video (HD-SDI). This mode is called Stand Alone Devices or Camera System Onchip.
01. DSP Digital Signal Processor
DSP (digital signal processor) is a unique microprocessor with its own complete instruction system. It is a device that processes a large amount of information with digital signals. Its biggest feature is that it has a dedicated hardware multiplier and Harvard bus structure to process a large number of digital signals quickly.
A digital signal processor includes a control unit, an operation unit, various registers and a certain number of storage units in a small chip. It can also be connected with a number of memories on its periphery, and can communicate with a certain number of external devices. It has comprehensive functions of software and hardware, and is itself a microcomputer.
DSP adopts Harvard design, det vil si, the data bus and address bus are separated, so that the program and data are stored in two separate spaces, allowing for complete overlap of fetching instructions and executing instructions. That is to say, when executing the last instruction, the next instruction can be taken out and decoded, which greatly improves the speed of the microprocessor. In addition, it allows transmission between program space and data space, because it increases the flexibility of devices.
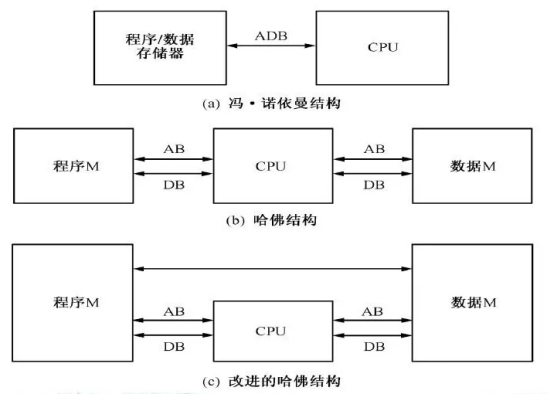
Its working principle is to receive analog signals, convert them into digital signals of 0 eller 1, modify, delete and strengthen the digital signals, and interpret the digital data back to analog data or actual environment format in other system chips. It not only has programmability, but also can run tens of millions of complex instructions per second in real time. Its source is more than general-purpose microprocessors. It is an increasingly important computer chip in the digital electronic world. Its powerful data processing ability and high running speed are the two most commendable features.
In today’s digital era, DSP has become the basic device in communication, computer, consumer electronics and other fields.
02. Features of DSP system
(1) Convenient interface
DSP system is compatible with other systems or devices based on modern digital technology. It is much easier to realize certain functions through such system interfaces than it is to interface analog systems with these systems.
(2) Easy programming
The programmable DSP chip of DSP system can enable designers to modify and upgrade the software flexibly and conveniently during the development process.
(3) Good stability
DSP system is based on digital processing, which is less affected by ambient temperature and noise, and has high reliability.
(4) High precision
16 bit digital system can achieve the accuracy.
(5) Good repeatability
The performance of the analog system is greatly affected by the performance of component parameters, while the digital system is basically unaffected, so the digital system is convenient for testing, debugging and mass production.
(6) Easy integration
Digital components in DSP system are highly standardized, which is convenient for large-scale integration.
Hard core science popularization Hard core science popularization Hard core science popularization Hard core science popularization Hard core science popularization Hard core science popularization Hard core science popularization Hard core science popularization
